Decreased energy production in thiamine deficiency – Biochemistry MCQ
Decreased energy production in thiamine deficiency is due to?
A. It is a cofactor for oxidative reduction
B. It is required for transamination reactions
C. It is a coenzyme for alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in citric acid cycle
D. It is a coenzyme for transketolase in hexose monophosphate shunt
Correct answer : C. It is a coenzyme for alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in citric acid cycle
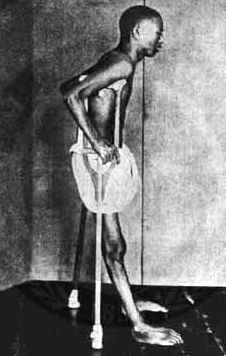 A patient suffering from beriberi
A patient suffering from beriberi
Thiamine – Properties, Functions and Deficiency disorders
- Thiamine (vitamin B1) is a water soluble vitamin
- Thiamine pyrophosphate acts as a coenzyme in the catabolism of carbohydrates and amino acids
- It is also required for the biosynthesis of acetylcholine and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA)
- Cereals are the important dietary sources of thiamine
- It is present in yeast extract and pork in very high concentrations
- It is important for energy production as it is a coenzyme for pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle / Tricarboxylic acid cycle)
- It is a also a coenzyme for transketolase in pentose phosphate pathway (involved in the production of NADPH)
- Deficiency of thiamine leads to Beriberi
- The major forms of beriberi are:
- Wet beriberi (cardiovascular disease)
- Dry beriberi (neurological disease)
- Infantile beriberi
- Alcoholics are prone to develop Wernicke’s encephalopathy due to deficiency of thiamine