Function of axonemal dynein – Physiology MCQ
The function of axonemal dynein is?
A. Moves particles to the ‘minus’ end of microtubule.
B. Binds to actin and produce motion by bending their neck region.
C. Responsible for the beating of flagella and cilia.
D. Moves particles towards ‘plus’ end of microtubule.
Correct answer : C. Responsible for the beating of flagella and cilia.
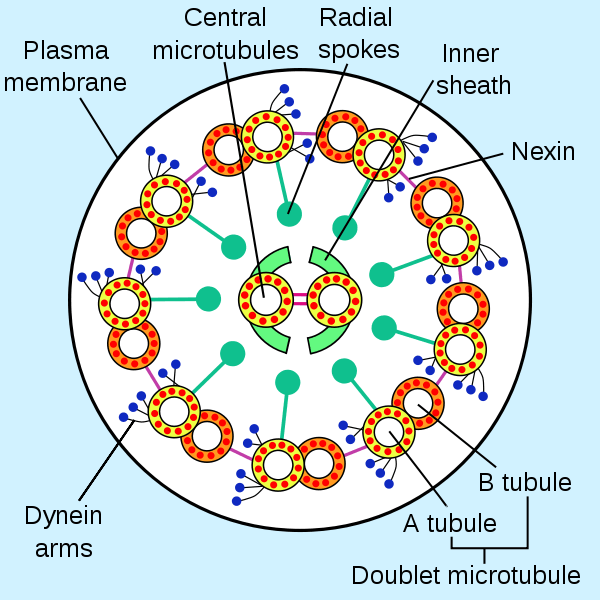 Eukaryotic flagellum showing the 9+2 arrangement of microtubules. Dynein arms (blue) are visible.
Eukaryotic flagellum showing the 9+2 arrangement of microtubules. Dynein arms (blue) are visible.
- Axonemal dynein oscillates and is responsible for the beating of flagella and cilia.
- Cytoplasmic dynein moves particles to the ‘minus‘ end of microtubule.
- Kinesin moves particles towards ‘plus‘ end of microtubule.
- Myosin II binds to actin and produce motion by bending their neck region.
Ref: Review of Medical Physiology, William F Ganong, 22nd edition, p14.
Image credits: Author: Smartse. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Eukaryotic_flagellum.svg




