Pleural effusion – left
Click on the image for an enlarged view
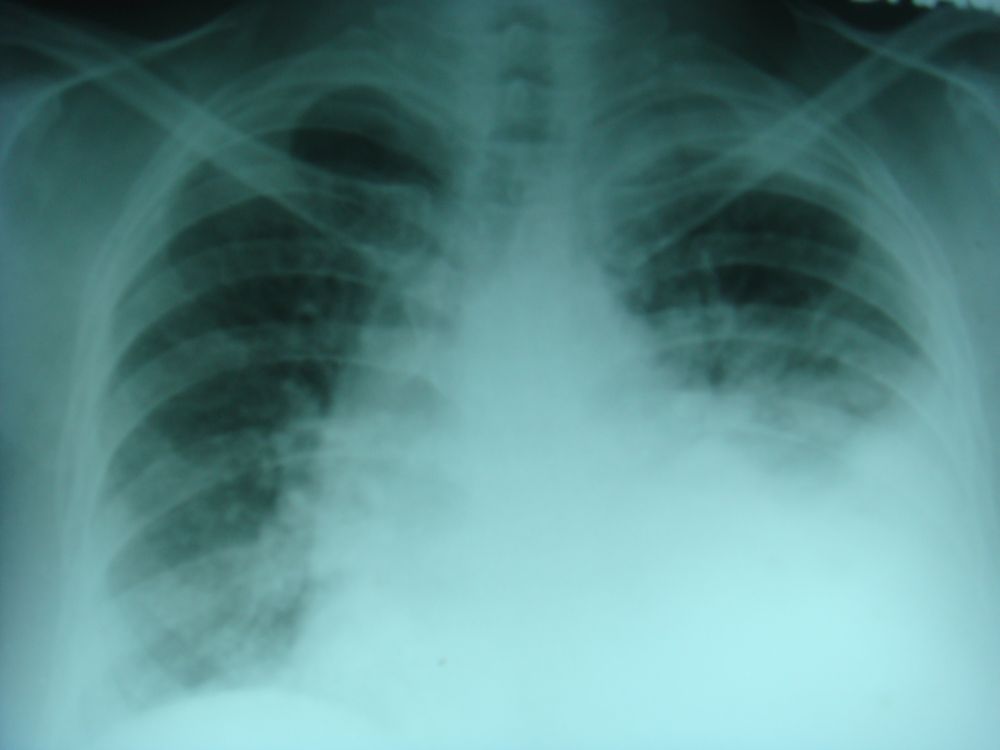
Homogenous opacity with higher level towards the axilla on the left side is characteristic of a large pleural effusion on the left side. Tracheal and mediastinal shift to the right side is also evident. Pleural effusion can be either a transudate as in heart failure or exudate as in infections, inflammatory disorders or malignancy. Transudate is identified as a clear fluid with low protein and cell content. Exudate is straw coloured and has high protein and cell count. Hemorrhagic effusion is seen in malignancies. Careful survey of the film for evidence of malignancies and rib erosion is needed. Pleural effusion in heart failure is most commonly bilateral. If it is unilateral, it is more common on right side, possibly because of larger surface area of the right lung permitting more transudation in heart failure.


