Unilateral papilledema
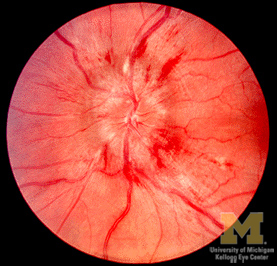
Fundus picture – Papilledema
Image by The eyes have it
- Papilledema is usually bilateral (See Why papilledema occurs bilaterally? )
- Under certain special circumstances, papilledema can be unilateral. They are:
- Foster Kennedy syndrome
- Intracranial lesions that exert pressure on one optic nerve often leads to unilateral optic atrophy
- If these lesions are large enough, they may cause increased intracranial tension and papilledema in the opposite eye
- Seen in :
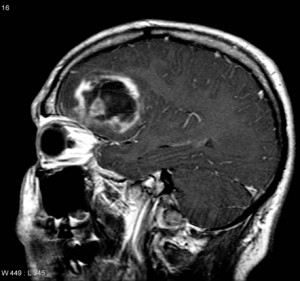
- olfactory groove meningiomas
- frontal lobe tumours
- Pseudo Foster Kennedy syndrome
- Increased intracranial pressure with ppre existingunilateral optic atrophy (due to any cause) again results in unilateral papilledema of opposite eye
- Foster Kennedy syndrome
Frontal lobe tumour – MRI. (Frontal lobe tumours can cause unilateral papilledema)
Image courtesy of Radiopaedia.org (the whole case can be seen here)