Juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis – Etiology, Pathology, Clinical Features, Management
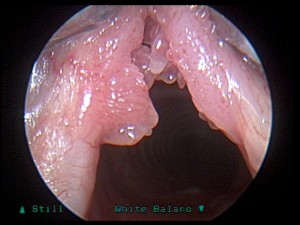
Bilateral Laryngeal Papilloma
- Laryngeal papillomas constitute 80% of the neoplastic lesions of the larynx
- Juvenile laryngeal papillomas are a type of squamous papillomas seen in infants and children
Etiology:
- It is believed to be viral in origin (Human papilloma virus)
- Association with maternal condylomata acuminata is seen
Pathology:
- Proliferation of squamous epithelium
Sites involved:
- Epiglottis
- True vocal cords
- False vocal cords
- Other areas of larynx
- Trachea
Clinical Features:
- Hoarseness of voice
- Stridor
Treatment:
- Endoscopic removal by cup forceps
- Cryotherapy
- Microelectrocautery
- CO2 laser – preferred method – less bleeding, precise removal possible
Recurrence:
- There is high chance of recurrence
- Interferon therapy is useful in preventing recurrence
Image credits: Otolaryngology Houston
One Comment



please suggest how i prepare for entrance examination
and which book i prefer for itt
thankyou…